Givet et tal n, find alle binære sekvenser af længden 2n, således at summen af første n bit er den samme som summen af sidste n bit.
Eksempler:
hvor er indsæt nøgle på laptop tastatur
Input: N = 2 Output: 0101 1111 1001 0110 0000 1010 Input: N = 3 Output: 011011 001001 011101 010001 101011 111111 110011 101101 100001 110101 001010 011110 010010 001100 000000 010100 101110 100010 110110 100100
Ideen er at rette første og sidste bit og derefter gentages for de resterende 2*(n-1) bits. Der er fire muligheder, når vi ordner første og sidste bit -
- Første og sidste bit er 1 resterende n - 1 bit på begge sider skal også have samme sum.
- Første og sidste bit er 0 resterende n - 1 bit på begge sider skal også have samme sum.
- Første bit er 1 og sidste bit er 0 summen af resterende n - 1 bit på venstre side bør være 1 mindre end summen af n-1 bit på højre side.
- Første bit er 0 og sidste bit er 1 sum af resterende n - 1 bit på venstre side bør være 1 mere end summen af n-1 bit på højre side.
Nedenfor er implementering af ovenstående idé -
// C++ program to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same #include
// Java program to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and second // half bits is same import java.io.*; import java.util.*; class GFG { // Function to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index static void findAllSequences(int diff char out[] int start int end) { // We can't cover difference of more // than n with 2n bits if (Math.abs(diff) > (end - start + 1) / 2) return; // if all bits are filled if (start > end) { // if sum of first n bits and // last n bits are same if (diff == 0) { System.out.print(out); System.out.print(' '); } return; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 out[start] = '0'; out[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff + 1 out start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 1 out[start] = out[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff out start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 0 out[start] = out[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff out start + 1 end - 1); // fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 out[start] = '1'; out[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff - 1 out start + 1 end - 1); } // Driver program public static void main (String[] args) { // input number int n = 2; // allocate string containing 2*n characters char[] out = new char[2 * n + 1]; // null terminate output array out[2 * n] = '�'; findAllSequences(0 out 0 2*n - 1); } } // This code is contributed by Pramod Kumar
# Python3 program to print even length binary sequences # whose sum of first and second half bits is same # Function to print even length binary sequences # whose sum of first and second half bits is same # diff --> difference between sums of first n bits # and last n bits # out --> output array # start --> starting index # end --> ending index def findAllSequences(diff out start end): # We can't cover difference of more than n with 2n bits if (abs(diff) > (end - start + 1) // 2): return; # if all bits are filled if (start > end): # if sum of first n bits and last n bits are same if (diff == 0): print(''.join(list(out))end=' '); return; # fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 out[start] = '0'; out[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff + 1 out start + 1 end - 1); # fill first and last bits as 1 out[start] = out[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff out start + 1 end - 1); # fill first and last bits as 0 out[start] = out[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff out start + 1 end - 1); # fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 out[start] = '1'; out[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff - 1 out start + 1 end - 1); # Driver program # input number n = 2; # allocate string containing 2*n characters out=['']*(2*n); findAllSequences(0 out 0 2*n - 1); # This code is contributed by mits
// C# program to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and second // half bits is same using System; class GFG { // Function to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and // second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of // first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index static void findAllSequences(int diff char []outt int start int end) { // We can't cover difference of // more than n with 2n bits if (Math.Abs(diff) > (end - start + 1) / 2) return; // if all bits are filled if (start > end) { // if sum of first n bits and // last n bits are same if (diff == 0) { Console.Write(outt); Console.Write(' '); } return; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit // as 1 outt[start] = '0'; outt[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff + 1 outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 1 outt[start] = outt[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 0 outt[start] = outt[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first bit as 1 and last // bit as 0 outt[start] = '1'; outt[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff - 1 outt start + 1 end - 1); } // Driver program public static void Main () { // input number int n = 2; // allocate string containing 2*n // characters char []outt = new char[2 * n + 1]; // null terminate output array outt[2 * n] = '�'; findAllSequences(0 outt 0 2*n - 1); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal.
// PHP program to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // Function to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index function findAllSequences($diff $out $start $end) { // We can't cover difference of more than n with 2n bits if (abs($diff) > (int)(($end - $start + 1) / 2)) return; // if all bits are filled if ($start > $end) { // if sum of first n bits and last n bits are same if ($diff == 0) print(implode(''$out).' '); return; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 $out[$start] = '0'; $out[$end] = '1'; findAllSequences($diff + 1 $out $start + 1 $end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 1 $out[$start] = $out[$end] = '1'; findAllSequences($diff $out $start + 1 $end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 0 $out[$start] = $out[$end] = '0'; findAllSequences($diff $out $start + 1 $end - 1); // fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 $out[$start] = '1'; $out[$end] = '0'; findAllSequences($diff - 1 $out $start + 1 $end - 1); } // Driver program // input number $n = 2; // allocate string containing 2*n characters $out=array_fill(02*$n''); findAllSequences(0 $out 0 2*$n - 1); // This code is contributed by chandan_jnu ?> <script> // JavaScript program to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and second // half bits is same // Function to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and // second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of // first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index function findAllSequences(diff outt start end) { // We can't cover difference of // more than n with 2n bits if (Math.abs(diff) > parseInt((end - start + 1) / 2 10)) return; // if all bits are filled if (start > end) { // if sum of first n bits and // last n bits are same if (diff == 0) { document.write(outt.join('')); document.write(' '); } return; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit // as 1 outt[start] = '0'; outt[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff + 1 outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 1 outt[start] = outt[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 0 outt[start] = outt[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first bit as 1 and last // bit as 0 outt[start] = '1'; outt[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff - 1 outt start + 1 end - 1); } // input number let n = 2; // allocate string containing 2*n // characters let outt = new Array(2 * n + 1); // null terminate output array outt[2 * n] = '�'; findAllSequences(0 outt 0 2*n - 1); </script>
Produktion
0101 1111 1001 0110 0000 1010
Tidskompleksitet: O((4 ^ N )* N)
4^N på grund af 4 rekursive opkald og N (forenklet fra 2N) for tid brugt på at udskrive strenge i størrelse 2N
Hjælpeplads: PÅ)
Der er en anden tilgang, hvorved vi genererer alle mulige strenge med længden n og gemmer dem i en liste ved et indeks, der repræsenterer deres sum. Derefter itererer vi gennem hver liste og genererer strengene i størrelse 2n ved at udskrive hver streng med alle andre strenge på listen, der lægger op til den samme værdi.
C++// C++ program to implement the approach #include
// Java program to implement the approach import java.util.*; class GFG { // function that finds all the subsequences static void findAllSequences(int n) { ArrayList<ArrayList<String> > sumToString = new ArrayList<ArrayList<String> >(); for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) { sumToString.add( new ArrayList<String>()); // list of strings // where index // represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum( n sumToString new ArrayList<String>() 0); permuteSequences(sumToString); } static void generateSequencesWithSum( int n ArrayList<ArrayList<String> > sumToString ArrayList<String> sequence int sumSoFar) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to // include if (n == 0) { // add permutation to list of sequences with sum // corresponding to index String seq = ''; for (int i = 0; i < sequence.size(); i++) { seq = seq + sequence.get(i); } ArrayList<String> x = sumToString.get(sumSoFar); x.add(seq); sumToString.set(sumSoFar x); return; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence.add('0'); generateSequencesWithSum(n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar); sequence.remove(0); // Generate sequence +1 sequence.add('1'); generateSequencesWithSum(n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar + 1); sequence.remove(0); } // function to form permutations of the sequences static void permuteSequences( ArrayList<ArrayList<String> > sumToString) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for (int sumIndexArr = 0; sumIndexArr < sumToString.size(); sumIndexArr++) { // Append for (int sequence1 = 0; sequence1 < sumToString.get(sumIndexArr).size(); sequence1++) { for (int sequence2 = 0; sequence2 < sumToString.get(sumIndexArr).size(); sequence2++) { if (sumIndexArr == sumToString.size() - 1 && sequence1 == sumToString .get(sumIndexArr) .size() - 1 && sequence2 == sumToString .get(sumIndexArr) .size() - 1) { System.out.print('1111'); } else { System.out.println( sumToString.get(sumIndexArr) .get(sequence1) + sumToString.get(sumIndexArr) .get(sequence2)); } } } } } // Driver Code public static void main(String[] args) { // Function Call findAllSequences(2); } // this code is contributed by phasing17 }
def findAllSequences(n): sumToString = [[] for x in range(n+1)] # list of strings where index represents sum generateSequencesWithSum(n sumToString [] 0) permuteSequences(sumToString) def generateSequencesWithSum(n sumToString sequence sumSoFar): #Base case if there are no more binary digits to include if n == 0: sumToString[sumSoFar].append(''.join(sequence)) #add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index return #Generate sequence +0 sequence.append('0') generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar) sequence.pop() #Generate sequence +1 sequence.append('1') generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar+1) sequence.pop() def permuteSequences(sumToString): #There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for sumIndexArr in sumToString: # Append for sequence1 in sumIndexArr: for sequence2 in sumIndexArr: print(sequence1 + sequence2) findAllSequences(2) #Contribution by Xavier Jean Baptiste
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GFG { static void findAllSequences(int n) { List<List<string>> sumToString = new List<List<string>>(); for(int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) { sumToString.Add(new List<string>()); // list of strings where index represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum(n sumToString new List<string>() 0); permuteSequences(sumToString); } static void generateSequencesWithSum(int n List<List<string>> sumToString List<string> sequence int sumSoFar) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to include if(n == 0) { //add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index string seq = ''; for(int i = 0; i < sequence.Count; i++) { seq = seq + sequence[i]; } sumToString[sumSoFar].Add(seq); return; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence.Add('0'); generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar); sequence.RemoveAt(0); // Generate sequence +1 sequence.Add('1'); generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar+1); sequence.RemoveAt(0); } static void permuteSequences(List<List<string>> sumToString) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for(int sumIndexArr = 0; sumIndexArr < sumToString.Count; sumIndexArr++) { // Append for(int sequence1 = 0; sequence1 < sumToString[sumIndexArr].Count; sequence1++) { for(int sequence2 = 0; sequence2 < sumToString[sumIndexArr].Count; sequence2++) { if(sumIndexArr == sumToString.Count-1 && sequence1 == sumToString[sumIndexArr].Count-1 && sequence2 == sumToString[sumIndexArr].Count-1) { Console.Write('1111'); } else { Console.WriteLine(sumToString[sumIndexArr][sequence1] + sumToString[sumIndexArr][sequence2]); } } } } } static void Main() { findAllSequences(2); } } // This code is contributed by divyesh072019.
<script> function findAllSequences(n) { let sumToString = []; for(let i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) { sumToString.push([]); // list of strings where index represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum(n sumToString [] 0); permuteSequences(sumToString); } function generateSequencesWithSum(n sumToString sequence sumSoFar) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to include if(n == 0) { //add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index sumToString[sumSoFar].push(sequence.join('')); return; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence.push('0'); generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar); sequence.shift(); // Generate sequence +1 sequence.push('1'); generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar+1); sequence.shift(); } function permuteSequences(sumToString) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for(let sumIndexArr = 0; sumIndexArr < sumToString.length; sumIndexArr++) { // Append for(let sequence1 = 0; sequence1 < sumToString[sumIndexArr].length; sequence1++) { for(let sequence2 = 0; sequence2 < sumToString[sumIndexArr].length; sequence2++) { if(sumIndexArr == sumToString.length-1 && sequence1 == sumToString[sumIndexArr].length-1 && sequence2 == sumToString[sumIndexArr].length-1) { document.write('1111'); } else { document.write(sumToString[sumIndexArr][sequence1] + sumToString[sumIndexArr][sequence2] + ''); } } } } } findAllSequences(2); // This code is contributed by decode2207. </script>
Produktion
0000 0101 0110 1001 1010 1111
Tidskompleksitetsanalyse:
generer SequencesWithSum = O((2N)*N)
- 2N: vi genererer al permutation af binære strenge af størrelse N
- N: konverter listen over tegn til en streng og gem den i array. Dette gøres i basissagen.
permuteSequences = O((2N) * N!/(N/2)!2*N)
- 2N: vi itererer gennem hele strengen genereret af størrelse n
- N!/(N/2)!2: Denne her er lidt udfordrende at forklare
lad os tage N = 2 som eksempel. Vores række af mulige sekvenser af størrelse n ville være:
| array indeks | 1 | 2 | |
| liste over strenge | 00 | 0110 | 11 |
I listen over strenge, hvor indekset repræsenterer summen, får vi antallet af strenge af størrelse 2n ved at bruge 'n vælg k'-formlen. I vores tilfælde ville det være nCk *nCk, hvor k repræsenterer antallet af 1'ere i hver halvdel af strengen af størrelse 2n:
k = 0 vi har (2C0)^2 = 1 streng (0000)
k = 1 vi har (2C1)^2 streng = 4 strenge(0101 0110 1001 1010)
k = 2 vi har (2c2)^2 = 1 streng (1111)
mylivecricket ind til live cricket
Vi får vores længste liste over strenge, når k = N/2 derforNCN/2= N!/[(N/2)! * (N - N/2)!] hvilket forenkler tilNCN/2= N!/(N/2)!2
Derfor må vi højst iterere igennem for hvert elementNCN/2til dannelse af strenge med længden 2N
Uden formelt bevis, hvis vi grafer 2^N og N!/(N/2)!2vi ser at 2Nhar en hurtigere vækstrate end sidstnævnte. Derfor O(2N* N!/(N/2)2)< O(2N*2N) = O(22n) = O(4N)
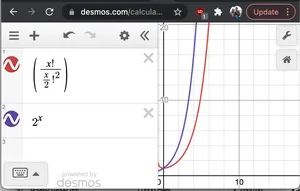 Graf af 2^x og nC(n/2)
Graf af 2^x og nC(n/2)- N: vi skal udskrive hver streng i størrelse 2N
Endelig kan vi ignorere tidskompleksiteten af generSequencesWithSum, fordi permuteSequence er det førende udtryk
Tidskompleksitet: O(2N* N!/(N/2)!2* N) (bedre end den første opløsning af O((4^N) * N se forklaring ovenfor for yderligere detaljer)
Hjælpeplads : O(2N), fordi vi gemmer alle binære strengpermutationer af størrelse N
'murerens formel'
#include
import java.util.*; class GFG { static class FirstHalf { String data; int sum; FirstHalf(String data int sum) { this.data = data; this.sum = sum; } } //MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum static Map<Integer ArrayList<String>> map = new HashMap<>(); //first N-half bits static List<FirstHalf> firstHalf = new ArrayList<>(); //function to find sum of the bits from a String public static int sumOfString(String s) { int sum = 0; //ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for(char c: s.toCharArray()) { sum += c - '0'; } return sum; } public static void perm(String p char[] bin int level int n) { //p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) //bin: {'0' '1'} //l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) //n: total levels if(level == 0) { //at solution level find sum of the current permutation int sum = sumOfString(p); //store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf.add(new FirstHalf(p sum)); //put current permutation to its respective sum value map.putIfAbsent(sum new ArrayList<String>()); map.get(sum).add(p); return; } //generate calls for permutation //working: first solution with all 0s then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for(char c: bin) { perm(p+c bin level-1 n); } } public static void result() { int i = 0; for(FirstHalf first: firstHalf) { //for each firstHalf string //find sum of the bits of current string int sum = first.sum; //retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key ArrayList<String> secondHalf = map.get(sum); for(String second: secondHalf) { //append first and second half and print System.out.print(first.data+second+' '); //after every 6 solution line is changed in output //only for formatting below lines could be removed i++; if(i % 6 == 0) System.out.println(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { char[] up = {'0' '1'}; int n = 2; perm('' up n n); result(); } } //Code contributed by Animesh Singh
# Python code implementation class FirstHalf: def __init__(self data sum): self.data = data self.sum = sum # MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum map = {} # first N-half bits firstHalf = [] # function to find sum of the bits from a String def sumOfString(s): sum = 0 # ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for i in range(len(s)): sum += ord(s[i]) - ord('0') return sum def perm(p bin level n): # p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) # bin: ['0' '1'] # l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) # n: total levels if level == 0: # at solution level find sum of the current permutation sum = sumOfString(p) # store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf.append(FirstHalf(p sum)) # put current permutation to its respective sum value if sum not in map: map[sum] = [] map[sum].append(p) return # generate calls for permutation # working: first solution with all 0s then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for i in range(len(bin)): perm(p+bin[i] bin level-1 n) def result(): i = 0 for j in range(len(firstHalf)): # for each firstHalf string # find sum of the bits of current string sum = firstHalf[j].sum # retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key secondHalf = map[sum] for k in range(len(secondHalf)): # append first and second half and print print(firstHalf[j].data + secondHalf[k] + ' ' end='') # after every 6 solution line is changed in output # only for formatting below lines could be removed i = i + 1 if(i % 6 == 0): print('n') up = ['0' '1'] n = 2 perm('' up n n) result() # The code is contributed by Nidhi goel.
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class FirstHalf { public string data; public int sum; public FirstHalf(string data int sum) { this.data = data; this.sum = sum; } } class Gfg { // MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum static Dictionary<int List<string>> mp = new Dictionary<int List<string>>(); // first N-half bits static List<FirstHalf> firstHalf = new List<FirstHalf>(); // function to find sum of the bits from a String static int sumOfString(string s) { int sum = 0; // ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) foreach (char c in s) { sum += (c - '0'); } return sum; } static void perm(string p char[] bin int level int n) { // p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) // bin: {'0' '1'} // l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) // n: total levels if (level == 0) { // at solution level find sum of the current permutation int sum = sumOfString(p); // store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf.Add(new FirstHalf(p sum)); // put current permutation to its respective sum value if (mp.ContainsKey(sum)) { mp[sum].Add(p); } else { mp.Add(sum new List<string> { p }); } return; } // generate calls for permutation // working: first solution with all 0s // then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { char c = bin[i]; perm(p + c bin level - 1 n); } } static void result() { int i = 0; foreach (FirstHalf first in firstHalf) { // for each firstHalf string // find sum of the bits of current string int sum = first.sum; // retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key List<string> secondHalf = mp[sum]; foreach (string second in secondHalf) { // append first and second half and print Console.Write(first.data + second + ' '); // after every 6 solution line is changed in output // only for formatting below lines could be removed i++; if (i % 6 == 0) Console.WriteLine(); } } } static void Main(string[] args) { char[] up = { '0' '1' }; int n = 2; string x = ''; perm(x up n n); result(); } }
class FirstHalf { constructor(data sum) { this.data = data; this.sum = sum; } } // MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum const map = new Map(); // first N-half bits const firstHalf = []; // function to find sum of the bits from a String function sumOfString(s) { let sum = 0; //ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for(let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) { sum += s.charCodeAt(i) - '0'.charCodeAt(0); } return sum; } function perm(p bin level n) { // p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) // bin: ['0' '1'] // l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) // n: total levels if(level == 0) { // at solution level find sum of the current permutation let sum = sumOfString(p); // store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf.push(new FirstHalf(p sum)); // put current permutation to its respective sum value if(!map.has(sum)) map.set(sum []); map.get(sum).push(p); return; } // generate calls for permutation // working: first solution with all 0s then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for(let i = 0; i < bin.length; i++) { perm(p+bin[i] bin level-1 n); } } function result() { let i = 0; for(let j = 0; j < firstHalf.length; j++) { // for each firstHalf string // find sum of the bits of current string let sum = firstHalf[j].sum; // retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key let secondHalf = map.get(sum); for(let k = 0; k < secondHalf.length; k++) { // append first and second half and print process.stdout.write(firstHalf[j].data + secondHalf[k] + ' '); // after every 6 solution line is changed in output // only for formatting below lines could be removed i++; if(i % 6 == 0) process.stdout.write('n'); } } } const up = ['0' '1']; const n = 2; perm('' up n n); result();
Produktion
0000 0101 0110 1001 1010 1111
Algoritme:
1. Generer alle binære permutationer af størrelse n
2. Beregn summen af bits af hver permutation og husk det for anden halvdel
[for eksempel: for n=2 husk, at der er to strenge med sum = 1, dvs. '01' '10' ]
3. Iterér alle de genererede permutationer og tilføj den anden halvdel for hver af dem i henhold til summen af bits
Tidskompleksitetsanalyse:
tal for alfabetet
sumOfString() = O(N): gennemløb hver bit og add den til summen
perm() = O(2N*N)
2N * N: vi genererer alle permutationer af binære bits af størrelse N og finder summen af bits for hver permutation
resultat() = O((2N) * (N!/(N/2)!)2)
2N: vi itererer gennem alle mulige permutationer af størrelse N (første halvdel)
NCN/2 = N!/(N/2)!2: (anden halvdel maksimal størrelse): forklaring nedenfor:
lad os tage N = 4 som et eksempel.:
//Hash-Map ser ud
0 -> [0000] ................................(listestørrelse: 4C0 = 1)
1 -> [0001 0010 0100 1000] ................................(listestørrelse: 4C1 = 4)
2 -> [0011 0101 0110 1001 1010 1100] ................................(listestørrelse: 4C2 = 6)
3 -> [0111 1011 1101 1110] ................................(listestørrelse: 4C3 = 4)
4 -> [1111] ................................(listestørrelse: 4C4 = 1)
Vi observerer her, at hver liste har en størrelse på N vælg Nøgle, som vil være maksimal ved N vælg N/2
Da vi gentager alle de 2Npermutationer og tilføjelse af anden halvdel fra kortet. Kortet har den maksimale størrelse liste ved N/2 position.
Worst case forekommer i N/2 position, hvor vi skal krydse NCN/2 = N!/(N/2)!2permutationer.
entitetsrelationel
Tidskompleksitet: O(2N* N!/(N/2)!2)
Hjælperum: O(2N) fordi vi gemmer alle binære strengpermutationer af størrelse N
