Lister er en af de mest brugte datastrukturer i Python. Vi bliver ved med at bruge lister i mange forskellige applikationer, fra løsning af simple problemer til komplekse problemer. I Python erstatter lister arrays med fordele som:
- Dynamisk i størrelsen
- Kan gemme elementer af forskellige datatyper på en enkelt liste
Vi kan få adgang til dataene fra lister som bestilt; i modsætning til i sæt, vil dataene være uordnet. For at få adgang til dataene kan vi bruge flere måder at iterere gennem hvert element i en liste. Denne tutorial dækker alle måder med eksempler.
1. Sløjfer
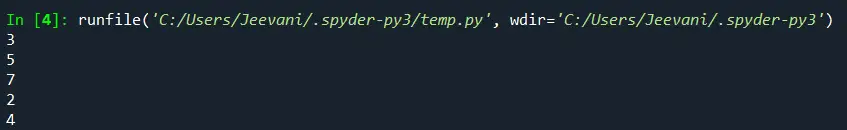
list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] count = 0 while (count <len(list1)): 1 print (list1 [count]) count="count" + < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p> <strong>Understanding:</strong> </p> <p>We created a list with a few elements. Initially, count = 0. We're printing the element at the 'count' index and incrementing the count in the while loop. When the count reaches the length of the list, the loop will be terminated, and all the elements will already be accessed.</p> <p> <strong>Mechanism:</strong> </p> <table class="table"> <tr> <td>count = 0</td> <td>list1 [0]</td> <td>3</td> </tr> <tr> <td>count = 1</td> <td>list1 [1]</td> <td>5</td> </tr> <tr> <td>count = 2</td> <td>list1 [2]</td> <td>7</td> </tr> <tr> <td>count = 3</td> <td>list1 [3]</td> <td>2</td> </tr> <tr> <td>count = 4</td> <td>list1 [4]</td> <td>4</td> </tr> <tr> <td>count = 5 = len (list1)</td> <td>-</td> <td>-</td> </tr> </table> <ul> <tr><td>Using for loop:</td> </tr></ul> <pre> list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] for i in list1: print (i) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python-2.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p> <strong>Understanding:</strong> </p> <p>Using for-in, we accessed all the i's, the elements inside the list.</p> <ul> <tr><td>Using for and range:</td> </tr></ul> <pre> list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] length = len (list1) for i in range (0, len (list1)): print (list1 [i]) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python-3.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p> <strong>Understanding:</strong> </p> <p>The range function helps the 'for' loop to iterate from 0 to the given list's length.</p> <p> <strong>Mechanism:</strong> </p> <table class="table"> <tr> <td>the range gives - 0</td> <td>list1 [0]</td> <td>3</td> </tr> <tr> <td>the range gives - 1</td> <td>list1 [1]</td> <td>5</td> </tr> <tr> <td>the range gives - 2</td> <td>list1 [2]</td> <td>7</td> </tr> <tr> <td>the range gives - 3</td> <td>list1 [3]</td> <td>2</td> </tr> <tr> <td>the range gives - 4</td> <td>list1 [4]</td> <td>4</td> </tr> </table> <ul> <li>The range function doesn't give the last element specified - len (list1) = 5 is not given.</li> </ul> <h2>2. Using List Comprehension</h2> <p>This is the simple and suggested way to iterate through a list in Python.</p> <p> <strong>Code:</strong> </p> <pre> list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] [print (i) for i in list1] print (' ') [print (list1 [i]) for i in range (0, len (list1))] print (' ') </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python-4.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p> <strong>Understanding:</strong> </p> <p>We can use for loops inside a list comprehension. We used the same for loops we used in the above examples but inside a list in a single line. This way, we can reduce the length of the code and also list comprehension is a very subtle and efficient way to put loops in lists.</p> <h2>3. Using enumerate():</h2> <p>The enumerate function converts the given list into a list of tuples. Another important fact about this function is that it keeps count of the iterations. This is a built-in function in Python.</p> <p> <strong>Code:</strong> </p> <pre> list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] for i, j in enumerate (list1): print ('index = ', i, 'value: ', j) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python-5.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <h2>4. Using lambda function and map():</h2> <p>These are anonymous functions. There is a function map () in Python that can accept a function as an argument, and it calls the function with every element in the iterable, and a new list with all the elements from the iterable will be returned.</p> <p> <strong>Code:</strong> </p> <pre> list1 = [3, 6, 1, 8, 7] result = list (map (lambda num: num, list1)) print (result) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python-6.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p> <strong>Understanding:</strong> </p> <p>The lambda num: num is given as an input to the map function along with the list. The function will take every single element in the list, accept it, and then return it. The map () function will pass the list elements one by one to the lambda function to return the elements.</p> <h2>What if we want to Iterate Multi-dimensional Lists?</h2> <p>There is an inbuilt module in Python designed to perform operations on multi-dimensional lists.</p> <p> <strong>1. To get numpy:</strong> </p> <p>Check if Python and pip are installed by opening the cmd via search and typing the commands:</p> <p> <strong>Python -version</strong> </p> <p> <strong>Pip --version</strong> </p> <p>If both Python and PIP are present in our system, it is now time to install our library:</p> <p> <strong>2. Open cmd from the start menu</strong> </p> <p> <strong>3. Type the command</strong> </p> <h3>pip install numpy</h3> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p>All the library packages, data, and sub-packages will be installed one after the other.</p> <p> <strong>Code:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy list1 = numpy. arange (9) list1 = list1. reshape (3, 3) for x in numpy. nditer (list1): print (x) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python-7.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p> <strong>Understanding:</strong> </p> <p>We imported the numpy module. Using the arrange method, we created an array with 9 elements. We accessed the list by reshaping it to 3 * 3 (rows * columns) using the reshape. Using the nditer function, we printed each element in the list.</p> <hr></len(list1)):>
Produktion:

Forståelse:
Ved at bruge for-in fik vi adgang til alle i'erne, elementerne på listen.
list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] length = len (list1) for i in range (0, len (list1)): print (list1 [i])
Produktion:

Forståelse:
Range-funktionen hjælper 'for'-løkken med at iterere fra 0 til den givne listes længde.
ascii tabel i c
Mekanisme:
| intervallet giver - 0 | ark1 [0] | 3 |
| intervallet giver - 1 | ark1 [1] | 5 |
| intervallet giver - 2 | ark1 [2] | 7 |
| intervallet giver - 3 | ark1 [3] | 2 |
| intervallet giver - 4 | ark1 [4] | 4 |
- Range-funktionen giver ikke det sidst specificerede element - len (liste1) = 5 er ikke givet.
2. Brug af listeforståelse
Dette er den enkle og foreslåede måde at gentage en liste i Python.
Kode:
list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] [print (i) for i in list1] print (' ') [print (list1 [i]) for i in range (0, len (list1))] print (' ')
Produktion:

Forståelse:
java arraylist sortering
Vi kan bruge til loops inde i en listeforståelse. Vi brugte det samme til sløjfer, vi brugte i ovenstående eksempler, men inde i en liste på en enkelt linje. På denne måde kan vi reducere længden af koden, og også listeforståelse er en meget subtil og effektiv måde at sætte loops i lister.
3. Brug enumerate():
Funktionen enumerate konverterer den givne liste til en liste over tupler. En anden vigtig kendsgerning ved denne funktion er, at den holder optælling af gentagelserne. Dette er en indbygget funktion i Python.
Kode:
list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] for i, j in enumerate (list1): print ('index = ', i, 'value: ', j)
Produktion:

4. Brug af lambda-funktion og map():
Det er anonyme funktioner. Der er et funktionskort () i Python, der kan acceptere en funktion som et argument, og det kalder funktionen med hvert element i iterablen, og en ny liste med alle elementerne fra iterablen vil blive returneret.
Kode:
list1 = [3, 6, 1, 8, 7] result = list (map (lambda num: num, list1)) print (result)
Produktion:

Forståelse:
Lambda num: num er givet som input til kortfunktionen sammen med listen. Funktionen vil tage hvert enkelt element i listen, acceptere det og derefter returnere det. Map ()-funktionen vil videregive listeelementerne et efter et til lambda-funktionen for at returnere elementerne.
Hvad hvis vi ønsker at gentage multidimensionelle lister?
Der er et indbygget modul i Python designet til at udføre operationer på multidimensionelle lister.
1. Sådan bliver du kvalme:
Tjek om Python og pip er installeret ved at åbne cmd'en via søgning og skrive kommandoerne:
Python -version
Pip --version
Hvis både Python og PIP er til stede i vores system, er det nu tid til at installere vores bibliotek:
2. Åbn cmd fra startmenuen
3. Indtast kommandoen
pip install numpy
Alle bibliotekspakker, data og underpakker vil blive installeret efter hinanden.
Kode:
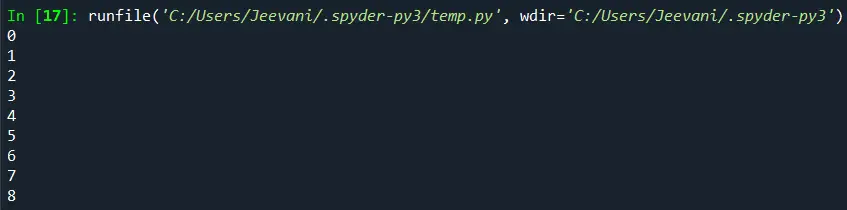
import numpy list1 = numpy. arange (9) list1 = list1. reshape (3, 3) for x in numpy. nditer (list1): print (x)
Produktion:
'abc' er i tal'
Forståelse:
Vi importerede numpy-modulet. Ved at bruge arrangementsmetoden oprettede vi et array med 9 elementer. Vi fik adgang til listen ved at omforme den til 3 * 3 (rækker * kolonner) ved hjælp af omformningen. Ved at bruge nditer-funktionen udskrev vi hvert element på listen.
