Det free() funktion i C bruges til at frigøre eller deallokere den dynamisk allokerede hukommelse og hjælper med at reducere hukommelsesspild. Det C fri() funktionen kan ikke bruges til at frigøre den statisk allokerede hukommelse (f.eks. lokale variabler) eller hukommelse allokeret på stakken. Den kan kun bruges til at deallokere heap-hukommelsen, der tidligere er allokeret ved hjælp af funktionerne malloc(), calloc() og realloc().
Funktionen free() er defineret inde header-fil.
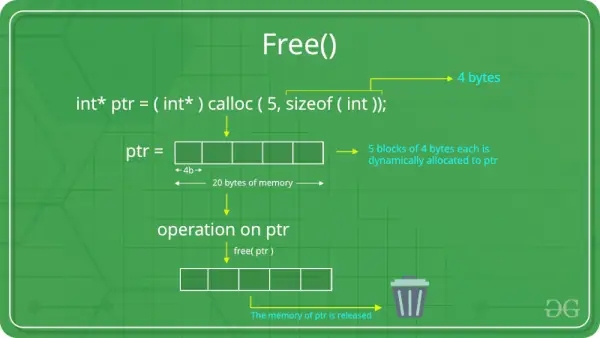
C free() Funktion
Syntaks for free() Funktion i C
void free (void * ptr );>
Parametre
- ptr er markøren til den hukommelsesblok, der skal frigøres eller deallokeres.
Returværdi
- Funktionen free() returnerer ikke nogen værdi.
Eksempler på gratis()
Eksempel 1:
Følgende C-program illustrerer brugen af calloc() funktion til at allokere hukommelse dynamisk og gratis() funktion for at frigive denne hukommelse.
C
betinget operator i java
// C program to demonstrate use of> // free() function using calloc()> #include> #include> int> main()> {> >// This pointer ptr will hold the> >// base address of the block created> >int>* ptr;> >int> n = 5;> >// Get the number of elements for the array> >printf>(>'Enter number of Elements: %d
'>, n);> >scanf>(>'%d'>, &n);> >// Dynamically allocate memory using calloc()> >ptr = (>int>*)>calloc>(n,>sizeof>(>int>));> >// Check if the memory has been successfully> >// allocated by calloc() or not> >if> (ptr == NULL) {> >printf>(>'Memory not allocated
'>);> >exit>(0);> >}> >// Memory has been Successfully allocated using calloc()> >printf>(>'Successfully allocated the memory using '> >'calloc().
'>);> >// Free the memory> >free>(ptr);> >printf>(>'Calloc Memory Successfully freed.'>);> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>Produktion
Enter number of Elements: 5 Successfully allocated the memory using calloc(). Calloc Memory Successfully freed.>
Eksempel 2:
Følgende C-program illustrerer brugen af malloc() funktion til at allokere hukommelse dynamisk og gratis() funktion for at frigive denne hukommelse.
C
// C program to demonstrate use of> // free() function using malloc()> #include> #include> int> main()> {> >// This pointer ptr will hold the> >// base address of the block created> >int>* ptr;> >int> n = 5;> >// Get the number of elements for the array> >printf>(>'Enter number of Elements: %d
'>, n);> >scanf>(>'%d'>, &n);> >// Dynamically allocate memory using malloc()> >ptr = (>int>*)>malloc>(n *>sizeof>(>int>));> >// Check if the memory has been successfully> >// allocated by malloc() or not> >if> (ptr == NULL) {> >printf>(>'Memory not allocated
'>);> >exit>(0);> >}> >// Memory has been Successfully allocated using malloc()> >printf>(>'Successfully allocated the memory using '> >'malloc().
'>);> >// Free the memory> >free>(ptr);> >printf>(>'Malloc Memory Successfully freed.'>);> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
hvordan man deaktiverer udviklertilstandProduktion
Enter number of Elements: 5 Successfully allocated the memory using malloc(). Malloc Memory Successfully freed.>
