 #practiceLinkDiv { display: ingen !important; }
#practiceLinkDiv { display: ingen !important; }Givet et binært træ, find længden af den længste sti, som består af noder med på hinanden følgende værdier i stigende rækkefølge. Hver knude betragtes som en sti med længde 1.
Eksempler:
In below diagram binary tree with longest consecutive path(LCP) are shown :
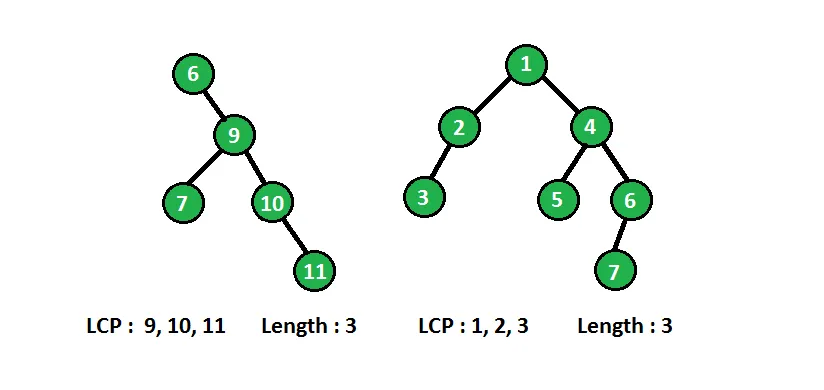
Vi kan løse ovenstående problem rekursivt. Ved hver knude har vi brug for information om dens overordnede knude, hvis den nuværende knude har en værdi mere end dens overordnede knude, så laver den en fortløbende sti ved hver knude, vi sammenligner knudepunktets værdi med dens overordnede værdi og opdaterer den længste på hinanden følgende sti i overensstemmelse hermed.
For at få værdien af den overordnede node vil vi videregive (node_value + 1) som et argument til den rekursive metode og sammenligne nodeværdien med denne argumentværdi, hvis den opfylder, opdatere den aktuelle længde af konsekutiv vej ellers geninitialisere den nuværende vejlængde med 1.
Se venligst nedenstående kode for bedre forståelse:
C++// C/C++ program to find longest consecutive // sequence in binary tree #include
// Java program to find longest consecutive // sequence in binary tree class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class Result { int res = 0; } class BinaryTree { Node root; // method returns length of longest consecutive // sequence rooted at node root int longestConsecutive(Node root) { if (root == null) return 0; Result res = new Result(); // call utility method with current length 0 longestConsecutiveUtil(root 0 root.data res); return res.res; } // Utility method to return length of longest // consecutive sequence of tree private void longestConsecutiveUtil(Node root int curlength int expected Result res) { if (root == null) return; // if root data has one more than its parent // then increase current length if (root.data == expected) curlength++; else curlength = 1; // update the maximum by current length res.res = Math.max(res.res curlength); // recursively call left and right subtree with // expected value 1 more than root data longestConsecutiveUtil(root.left curlength root.data + 1 res); longestConsecutiveUtil(root.right curlength root.data + 1 res); } // Driver code public static void main(String args[]) { BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree(); tree.root = new Node(6); tree.root.right = new Node(9); tree.root.right.left = new Node(7); tree.root.right.right = new Node(10); tree.root.right.right.right = new Node(11); System.out.println(tree.longestConsecutive(tree.root)); } } // This code is contributed by shubham96301
# Python3 program to find longest consecutive # sequence in binary tree # A utility class to create a node class newNode: def __init__(self data): self.data = data self.left = self.right = None # Utility method to return length of # longest consecutive sequence of tree def longestConsecutiveUtil(root curLength expected res): if (root == None): return # if root data has one more than its # parent then increase current length if (root.data == expected): curLength += 1 else: curLength = 1 # update the maximum by current length res[0] = max(res[0] curLength) # recursively call left and right subtree # with expected value 1 more than root data longestConsecutiveUtil(root.left curLength root.data + 1 res) longestConsecutiveUtil(root.right curLength root.data + 1 res) # method returns length of longest consecutive # sequence rooted at node root def longestConsecutive(root): if (root == None): return 0 res = [0] # call utility method with current length 0 longestConsecutiveUtil(root 0 root.data res) return res[0] # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': root = newNode(6) root.right = newNode(9) root.right.left = newNode(7) root.right.right = newNode(10) root.right.right.right = newNode(11) print(longestConsecutive(root)) # This code is contributed by PranchalK
// C# program to find longest consecutive // sequence in binary tree using System; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class Result { public int res = 0; } class GFG { Node root; // method returns length of longest consecutive // sequence rooted at node root int longestConsecutive(Node root) { if (root == null) return 0; Result res = new Result(); // call utility method with current length 0 longestConsecutiveUtil(root 0 root.data res); return res.res; } // Utility method to return length of longest // consecutive sequence of tree private void longestConsecutiveUtil(Node root int curlength int expected Result res) { if (root == null) return; // if root data has one more than its parent // then increase current length if (root.data == expected) curlength++; else curlength = 1; // update the maximum by current length res.res = Math.Max(res.res curlength); // recursively call left and right subtree with // expected value 1 more than root data longestConsecutiveUtil(root.left curlength root.data + 1 res); longestConsecutiveUtil(root.right curlength root.data + 1 res); } // Driver code public static void Main(String []args) { GFG tree = new GFG(); tree.root = new Node(6); tree.root.right = new Node(9); tree.root.right.left = new Node(7); tree.root.right.right = new Node(10); tree.root.right.right.right = new Node(11); Console.WriteLine(tree.longestConsecutive(tree.root)); } } // This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
<script> // JavaScript program to find longest consecutive // sequence in binary tree class Node { constructor(item) { this.data=item; this.left = this.right = null; } } let res = 0; let root; function longestConsecutive(root) { if (root == null) return 0; res=[0]; // call utility method with current length 0 longestConsecutiveUtil(root 0 root.data res); return res[0]; } // Utility method to return length of longest // consecutive sequence of tree function longestConsecutiveUtil(rootcurlength expectedres) { if (root == null) return; // if root data has one more than its parent // then increase current length if (root.data == expected) curlength++; else curlength = 1; // update the maximum by current length res[0] = Math.max(res[0] curlength); // recursively call left and right subtree with // expected value 1 more than root data longestConsecutiveUtil(root.left curlength root.data + 1 res); longestConsecutiveUtil(root.right curlength root.data + 1 res); } // Driver code root = new Node(6); root.right = new Node(9); root.right.left = new Node(7); root.right.right = new Node(10); root.right.right.right = new Node(11); document.write(longestConsecutive(root)); // This code is contributed by rag2127 </script>
Produktion
3
Tidskompleksitet: O(N) hvor N er antallet af noder i et givet binært træ.
Hjælpemellemrum: O(log(N))
Også diskuteret på nedenstående link:
Maksimal fortløbende stigende stilængde i binært træ
