Sløjfer i programmering bruges til at gentage en kodeblok, indtil den specificerede betingelse er opfyldt. En loop-sætning giver programmører mulighed for at udføre en sætning eller gruppe af sætninger flere gange uden gentagelse af kode.
string.compare c#
C
tilfældigt tal gen java
// C program to illustrate need of loops> #include> > int> main()> {> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> > >return> 0;> }> |
>
>Produktion
reagere inline stil
Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World>
Der er hovedsageligt to typer sløjfer i C-programmering:
- Entry Controlled Loops: I Entry Controlled Loops kontrolleres testtilstanden, før den går ind i hoveddelen af loopen. Til Loop og While Loop er Indgangskontrollerede sløjfer. Udgangskontrollerede sløjfer: I udgangskontrollerede sløjfer evalueres testtilstanden i slutningen af sløjfelegemet. Loopteksten vil køre mindst én gang, uanset om betingelsen er sand eller falsk. gør-mens-løkke er Exit Controlled loop.
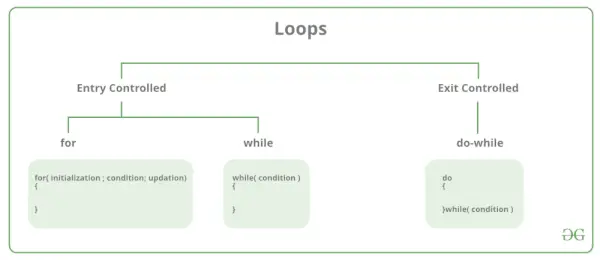
| Løkketype | Beskrivelse |
|---|---|
| for sløjfe | Initialiserer først, derefter tilstandstjek, udfører derefter brødteksten, og til sidst er opdateringen udført. |
| mens loop | Initialiserer først, derefter tilstandstjekker og udfører derefter kroppen, og opdatering kan være inde i kroppen. |
| gør-mens-løkke | do-while udfører først kroppen og derefter udføres tilstandskontrollen. |
for Loop
for loop in C-programmering er en gentagelseskontrolstruktur, der gør det muligt for programmører at skrive en loop, der vil blive udført et bestemt antal gange. for loop gør det muligt for programmører at udføre n antal trin sammen på en enkelt linje.
10 1 mio
Syntaks:
for (initialize expression; test expression; update expression) { // // body of for loop // }> Eksempel:
for(int i = 0; i In for loop, a loop variable is used to control the loop. Firstly we initialize the loop variable with some value, then check its test condition. If the statement is true then control will move to the body and the body of for loop will be executed. Steps will be repeated till the exit condition becomes true. If the test condition will be false then it will stop. Initialization Expression: In this expression, we assign a loop variable or loop counter to some value. for example: int i=1; Test Expression: In this expression, test conditions are performed. If the condition evaluates to true then the loop body will be executed and then an update of the loop variable is done. If the test expression becomes false then the control will exit from the loop. for example, i<=9; Update Expression: After execution of the loop body loop variable is updated by some value it could be incremented, decremented, multiplied, or divided by any value. for loop Equivalent Flow Diagram: Example: C // C program to illustrate for loop #include // Driver code int main() { int i = 0; for (i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { printf( 'Hello World
'); } return 0; } Output Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World While Loop While loop does not depend upon the number of iterations. In for loop the number of iterations was previously known to us but in the While loop, the execution is terminated on the basis of the test condition. If the test condition will become false then it will break from the while loop else body will be executed. Syntax: initialization_expression; while (test_expression) { // body of the while loop update_expression; } Flow Diagram for while loop: C // C program to illustrate // while loop #include // Driver code int main() { // Initialization expression int i = 2; // Test expression while(i <10) { // loop body printf( 'Hello World
'); // update expression i++; } return 0; } Output Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World do-while Loop The do-while loop is similar to a while loop but the only difference lies in the do-while loop test condition which is tested at the end of the body. In the do-while loop, the loop body will execute at least once irrespective of the test condition. Syntax: initialization_expression; do { // body of do-while loop update_expression; } while (test_expression); C // C program to illustrate // do-while loop #include // Driver code int main() { // Initialization expression int i = 2; do { // loop body printf( 'Hello World
'); // Update expression i++; // Test expression } while (i <1); return 0; } Output Hello World Above program will evaluate (i<1) as false since i = 2. But still, as it is a do-while loop the body will be executed once. Loop Control Statements Loop control statements in C programming are used to change execution from its normal sequence. Name Description break statement the break statement is used to terminate the switch and loop statement. It transfers the execution to the statement immediately following the loop or switch. continue statement continue statement skips the remainder body and immediately resets its condition before reiterating it. goto statement goto statement transfers the control to the labeled statement. Infinite Loop An infinite loop is executed when the test expression never becomes false and the body of the loop is executed repeatedly. A program is stuck in an Infinite loop when the condition is always true. Mostly this is an error that can be resolved by using Loop Control statements. Using for loop: C // C program to demonstrate infinite // loops using for loop #include // Driver code int main () { int i; // This is an infinite for loop // as the condition expression // is blank for ( ; ; ) { printf('This loop will run forever.
'); } return 0; } Output This loop will run forever. This loop will run forever. This loop will run forever. ... Using While loop: C // C program to demonstrate // infinite loop using while // loop #include // Driver code int main() { while (1) printf('This loop will run forever.
'); return 0; } Output This loop will run forever. This loop will run forever. This loop will run forever. ... Using the do-while loop: C // C program to demonstrate // infinite loop using do-while // loop #include // Driver code int main() { do { printf('This loop will run forever.
'); } while (1); return 0; } Output This loop will run forever. This loop will run forever. This loop will run forever. ...>