For at udføre input- og outputoperationer i C++ skal vi bruge iostream header-filer. Uden en header-fil kan vi ikke tage input fra brugeren eller udskrive noget output.
Syntaks for overskriftsfil:
#include #include 'iostream.h'
Der er to typer streams i iostream header-filen
scanner næste
1. Input Stream : For at tage input fra brugeren skal vi bruge cin, som hører til inputstrømmen
Syntaks for at bruge inputstrøm:
std::cin>>variable_name
Når cin udføres, vil markøren blive stoppet ved den pågældende sætning, indtil værdien er indtastet. Den indtastede værdi vil blive gemt i en variabel.
2. Output Stream : For at udskrive output bruger vi indbyggede funktioner i cout output-strømmen
Syntaks for cout
std::cout<<variable_name < pre> <p>When cout is executed, the value in the variable will be printed.</p> <h3>Different operations in iostream</h3> <p> <strong>1. Cin</strong> </p> <p>Using cin, we can take input from the user and store the value in the variable. We need to use the cin keyword followed by >> and the variable name.</p> <p> <strong>Syntax:</strong> </p> <pre> std::cin>>variable_name </pre> <p>To use cin, we need to use <strong>#include </strong> as cin belongs to this header file, and without this, an error will occur.</p> <p> <strong>Example code for cin:</strong> </p> <pre> //using header file iostream #include using namespace std; int main() { string name; //cin declaration cin >> name; return 0; } </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above code, we used cin to take the input, so to use cin, we included header file. When the input is taken, the string input is stored in the name variable.</p> <p> <strong>2. Cout</strong> </p> <p>To print the output, we need to use the cout keyword, which belongs to the iostream header file. To use cout, we need to use the cout keyword followed by << and variable or the statement to print the output.</p> <p>The syntax for using cout:</p> <pre> std::cout<<variable_name < pre> <p> <strong>Example of using cout:</strong> </p> <pre> //to use the cout statement, we need to use the iostream header file #include using namespace std; int main() { //cout statement is used here to print the statement cout << 'Hi from cout statement'; return 0;} </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-2.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation</strong> :</p> <p>In the above code, we used a cout statement to print the statement. To use the cout statement, we need to include iostream.h header file. Once the cout is executed, statement or variable value will be printing the output. To print any statement, we need to use double quotes (' '), and to print a variable value; we need to use just the variable name without double quotes(' ')</p> <p> <strong>3. Cerr</strong> </p> <p>Cerr is used to print errors in C++, which is present in the iostream header file. If we need to print any error message in the code if any condition fails, then cerr is very helpful.</p> <p>The syntax for cerr is:</p> <pre> cerr<<variable_name < pre> <p>Example:</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { int a; cin>>a; if(a%2==0){ cout<<'the number entered in even number'<<endl; } else{ std::cerr << 'enter proper number' '
'; return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-3.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above example, we used cin to take the input and check if the given number is even or not. If the given number is not even, we need to print an error that the given number is not an even number. We use the cerr keyword in the iostream header file to print this error.</p> <p> <strong>4. Clog:</strong> </p> <p>The clog is also used to print error messages, but unlike cerr, clog is buffered, which means the error message is stored in a buffer and then will be printed, but cerr is unbuffered and will not store the error message in the buffer. The clog also belongs to the iostream header file. As the clog is buffered, it will not show the error message immediately. The clog is preferred more than cerr when efficiency is more important.</p> <p>The syntax for clog:</p> <pre> clog<<variable_name; < pre> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { clog << 'This message is stored in the buffer'; return 0; } </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-4.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above code, we are printing an error. To print this error, we use cerr, which belongs to the iostream header file. Before printing the error, we store the error in a buffer.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> : For all the input and output streams</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { int a; string b; cin>>a; if(a%2==0){ cout<<'the number entered is even enter a name'<>b; cout< <b; } else{ std::cerr << 'enter even number' '
'; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-5.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation</strong> : In the above code, we used all the input and output streams in the iostream.h header file.</p> <hr></b;></'the></pre></variable_name;></pre></'the></pre></variable_name></pre></variable_name></pre></variable_name> For at bruge cin, skal vi bruge #omfatte da cin hører til denne header-fil, og uden denne vil der opstå en fejl.
Eksempelkode for cin:
//using header file iostream #include using namespace std; int main() { string name; //cin declaration cin >> name; return 0; } Produktion:
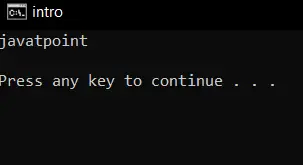
Forklaring:
I ovenstående kode brugte vi cin til at tage input, så for at bruge cin inkluderede vi header-fil. Når inputtet tages, lagres strenginputtet i navnevariablen.
2. Cout
For at udskrive outputtet skal vi bruge nøgleordet cout, som hører til iostream header-filen. For at bruge cout skal vi bruge nøgleordet cout efterfulgt af << og variabel eller sætningen for at udskrive output.
bias og varians
Syntaksen for at bruge cout:
std::cout<<variable_name < pre> <p> <strong>Example of using cout:</strong> </p> <pre> //to use the cout statement, we need to use the iostream header file #include using namespace std; int main() { //cout statement is used here to print the statement cout << 'Hi from cout statement'; return 0;} </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-2.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation</strong> :</p> <p>In the above code, we used a cout statement to print the statement. To use the cout statement, we need to include iostream.h header file. Once the cout is executed, statement or variable value will be printing the output. To print any statement, we need to use double quotes (' '), and to print a variable value; we need to use just the variable name without double quotes(' ')</p> <p> <strong>3. Cerr</strong> </p> <p>Cerr is used to print errors in C++, which is present in the iostream header file. If we need to print any error message in the code if any condition fails, then cerr is very helpful.</p> <p>The syntax for cerr is:</p> <pre> cerr<<variable_name < pre> <p>Example:</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { int a; cin>>a; if(a%2==0){ cout<<\'the number entered in even number\'<<endl; } else{ std::cerr << \'enter proper number\' \'
\'; return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-3.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above example, we used cin to take the input and check if the given number is even or not. If the given number is not even, we need to print an error that the given number is not an even number. We use the cerr keyword in the iostream header file to print this error.</p> <p> <strong>4. Clog:</strong> </p> <p>The clog is also used to print error messages, but unlike cerr, clog is buffered, which means the error message is stored in a buffer and then will be printed, but cerr is unbuffered and will not store the error message in the buffer. The clog also belongs to the iostream header file. As the clog is buffered, it will not show the error message immediately. The clog is preferred more than cerr when efficiency is more important.</p> <p>The syntax for clog:</p> <pre> clog<<variable_name; < pre> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { clog << 'This message is stored in the buffer'; return 0; } </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-4.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above code, we are printing an error. To print this error, we use cerr, which belongs to the iostream header file. Before printing the error, we store the error in a buffer.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> : For all the input and output streams</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { int a; string b; cin>>a; if(a%2==0){ cout<<\'the number entered is even enter a name\'<>b; cout< <b; } else{ std::cerr << \'enter even number\' \'
\'; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-5.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation</strong> : In the above code, we used all the input and output streams in the iostream.h header file.</p> <hr></b;></\'the></pre></variable_name;></pre></\'the></pre></variable_name></pre></variable_name> Produktion:

Forklaring :
I ovenstående kode brugte vi en cout-erklæring til at udskrive erklæringen. For at bruge cout-sætningen skal vi inkludere iostream.h header-fil. Når cout er udført, udskriver sætning eller variabel værdi outputtet. For at udskrive et udsagn, skal vi bruge dobbelte anførselstegn (' '), og at udskrive en variabel værdi; vi skal kun bruge variabelnavnet uden dobbelte anførselstegn(' ')
3. Cerr
Cerr bruges til at udskrive fejl i C++, som er til stede i iostream header-filen. Hvis vi har brug for at udskrive en fejlmeddelelse i koden, hvis en tilstand fejler, så er cerr meget nyttig.
Syntaksen for cerr er:
cerr<<variable_name < pre> <p>Example:</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { int a; cin>>a; if(a%2==0){ cout<<\'the number entered in even number\'<<endl; } else{ std::cerr << \'enter proper number\' \'
\'; return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-3.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above example, we used cin to take the input and check if the given number is even or not. If the given number is not even, we need to print an error that the given number is not an even number. We use the cerr keyword in the iostream header file to print this error.</p> <p> <strong>4. Clog:</strong> </p> <p>The clog is also used to print error messages, but unlike cerr, clog is buffered, which means the error message is stored in a buffer and then will be printed, but cerr is unbuffered and will not store the error message in the buffer. The clog also belongs to the iostream header file. As the clog is buffered, it will not show the error message immediately. The clog is preferred more than cerr when efficiency is more important.</p> <p>The syntax for clog:</p> <pre> clog<<variable_name; < pre> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { clog << 'This message is stored in the buffer'; return 0; } </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-4.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above code, we are printing an error. To print this error, we use cerr, which belongs to the iostream header file. Before printing the error, we store the error in a buffer.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> : For all the input and output streams</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { int a; string b; cin>>a; if(a%2==0){ cout<<\'the number entered is even enter a name\'<>b; cout< <b; } else{ std::cerr << \'enter even number\' \'
\'; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-5.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation</strong> : In the above code, we used all the input and output streams in the iostream.h header file.</p> <hr></b;></\'the></pre></variable_name;></pre></\'the></pre></variable_name> Produktion:
ændre fil linux

Forklaring:
I ovenstående kode udskriver vi en fejl. For at udskrive denne fejl bruger vi cerr, som hører til iostream header-filen. Inden fejlen udskrives, gemmer vi fejlen i en buffer.
Eksempel : For alle input- og outputstrømme
#include using namespace std; int main() { int a; string b; cin>>a; if(a%2==0){ cout<<\\'the number entered is even enter a name\\'<>b; cout< <b; } else{ std::cerr << \\'enter even number\\' \\'
\\'; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-5.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation</strong> : In the above code, we used all the input and output streams in the iostream.h header file.</p> <hr></b;></\\'the>