Eulers Totient-funktion Φ(n) for et input n er antallet af tal i {1, 2, 3, …, n-1}, der er relativt prime til n, dvs. de tal, hvis GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) med n er 1.
Eksempler:
Φ(1) = 1
gcd(1, 1) er 1
Φ(2) = 1
gcd(1, 2) er 1, men gcd(2, 2) er 2.
Φ(3) = 2
gcd(1, 3) er 1 og gcd(2, 3) er 1
Φ(4) = 2
gcd(1, 4) er 1 og gcd(3, 4) er 1
Φ(5) = 4
gcd(1, 5) er 1, gcd(2, 5) er 1,
gcd(3, 5) er 1 og gcd(4, 5) er 1
Φ(6) = 2
gcd(1, 6) er 1 og gcd(5, 6) er 1,
Anbefalet praksis Euler Totient-funktion Prøv det!
Hvordan beregner man Φ(n) for et input n?
EN enkel løsning er at iterere gennem alle tal fra 1 til n-1 og tælle tal med gcd med n som 1. Nedenfor er implementeringen af den simple metode til at beregne Eulers Totient-funktion for et input-heltal n.
// A simple C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Java // A simple java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi(int n) { int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by sunnusingh>Python3 # A simple Python3 program # to calculate Euler's # Totient Function # Function to return # gcd of a and b def gcd(a, b): if (a == 0): return b return gcd(b % a, a) # A simple method to evaluate # Euler Totient Function def phi(n): result = 1 for i in range(2, n): if (gcd(i, n) == 1): result+=1 return result # Driver Code for n in range(1, 11): print('phi(',n,') = ', phi(n), sep = '') # This code is contributed # by Smitha>C# // A simple C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi(int n) { int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void Main() { for (int n = 1; n <= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal>Javascript >PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // Function to return // gcd of a and b function gcd($a, $b) { if ($a == 0) return $b; return gcd($b % $a, $a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function function phi($n) { $result = 1; for ($i = 2; $i <$n; $i++) if (gcd($i, $n) == 1) $result++; return $result; } // Driver Code for ($n = 1; $n <= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(' .$n. ') =' . phi($n).'
'; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ>>C++ // A simple C++ program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function #include using namespace std; // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) cout << 'phi('< Produktion
phi(1) = 1 phi(2) = 1 phi(3) = 2 phi(4) = 2 phi(5) = 4 phi(6) = 2 phi(7) = 6 phi(8) = 4 phi( 9) = 6 phi(10) = 4
Ovenstående kode kalder gcd-funktionen O(n) gange. Tidskompleksiteten af gcd-funktionen er O(h), hvor h er antallet af cifre i et mindre antal af givne to tal. Derfor er en øvre grænse på tidskompleksitet af ovenstående løsning er O(N^2 log N) [Hvordan Φ kan der højst være Log10n cifre i alle tal fra 1 til n]
Hjælpeplads: O(log N)
Nedenfor er en Bedre løsning . Ideen er baseret på Eulers produktformel, som siger, at værdien af totientfunktioner er under produktets overordnede primfaktorer p af n.
download youtube video vlc
Formlen siger grundlæggende, at værdien af Φ(n) er lig med n ganget biprodukt af (1 – 1/p) for alle primfaktorer p af n. For eksempel værdien af Φ(6) = 6 * (1-1/2) * (1 – 1/3) = 2.
Vi kan finde alle primære faktorer ved at bruge ideen, der er brugt i det her stolpe.
1) Initialiser: resultat = n
2) Kør en løkke fra 'p' = 2 til sqrt(n), gør følgende for hver 'p'.
a) Hvis p deler n, så
Sæt: resultat = resultat * (1,0 - (1,0 / (float) p));
Opdel alle forekomster af p i n.
3) Returner resultat
Nedenfor er implementeringen af Eulers produktformel.
// C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function using Euler's // product formula #include using namespace std; int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and for every prime factor p, // multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for(int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat / n; //Da i mængden {1,2,....,n-1} er alle tal relativt prime med n //hvis n er et primtal returnerer (int)resultat; } // Driverkode int main() { int n; for(n = 1; n<= 10; n++) { cout << 'Phi' << '(' << n << ')' << ' = ' << phi(n) <C // C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula #include int phi(int n) { float result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat / n; //Da i mængden {1,2,....,n-1} er alle tal relativt prime med n //hvis n er et primtal returnerer (int)resultat; } // Driverprogram til at teste ovenstående funktion int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Java // Java program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n and for // every prime factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat / n; //Da i mængden {1,2,....,n-1} er alle tal relativt prime med n //hvis n er et primtal returnerer (int)resultat; } // Driverprogram til at teste ovenstående funktion public static void main(String args[]) { int n; for (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.>Python3 # Python 3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function # using Euler's product formula def phi(n) : result = n # Initialize result as n # Consider all prime factors # of n and for every prime # factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1 / p) p = 2 while p * p<= n : # Check if p is a prime factor. if n % p == 0 : # If yes, then update n and result while n % p == 0 : n = n // p result = result * (1.0 - (1.0 / float(p))) p = p + 1 # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most one # such prime factor) if n>1 : resultat -= resultat // n #Da i sættet {1,2,....,n-1} er alle tal relativt prime med n #hvis n er et primtal returner int(result) # Driver program til at teste ovenstående funktion for n i området(1, 11): print('phi(', n, ') = ', phi(n)) # Denne kode er bidraget # af Nikita Tiwari.>C# // C# program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula using System; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1 / p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (float)(1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat / n; //Da i mængden {1,2,....,n-1} er alle tal relativt prime med n //hvis n er et primtal returnerer (int)resultat; } // Driver Code public static void Main() { int n; for (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal.>Javascript // Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi(n) { // Initialize result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat / n; //Da i sættet {1,2,....,n-1} er alle tal relativt prime med n //hvis n er et primtal returner parseInt(result); } // Driverkode for (lad n = 1; n<= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} `); // This code is contributed by _saurabh_jaiswal>PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi($n) { // Initialize result as n $result = $n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for ($p = 2; $p * $p <= $n; ++$p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ($n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while ($n % $p == 0) $n /= $p; $result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / $p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ($n>1) $result -= $result / $n; //Da i sættet {1,2,....,n-1} er alle tal relativt prime med n //hvis n er et primtal returinterval($result); } // Driverkode for ($n = 1; $n<= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(' .$n. ') =' . phi($n).'
'; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ>> Produktion
Phi(1) = 1 Phi(2) = 1 Phi(3) = 2 Phi(4) = 2 Phi(5) = 4 Phi(6) = 2 Phi(7) = 6 Phi(8) = 4 Phi( 9) = 6 Phi(10) = 4
Tidskompleksitet: O(Φ n log n)
Hjælpeplads: O(1)
Vi kan undgå floating-point beregninger i ovenstående metode. Ideen er at tælle alle primfaktorer og deres multipla og trække dette tælling fra n for at få totientfunktionsværdien (primtalsfaktorer og multipla af primfaktorer vil ikke have gcd som 1)
1) Initialiser resultatet som n
2) Overvej hvert tal 'p' (hvor 'p' varierer fra 2 til Φ(n)).
Hvis p deler n, så gør følgende
a) Træk alle multipla af p fra 1 til n [alle multipla af p
vil have gcd mere end 1 (mindst p) med n]
b) Opdater n ved gentagne gange at dividere det med p.
3) Hvis det reducerede n er mere end 1, skal du fjerne alle multipla
af n fra resultat.
Nedenfor er implementeringen af ovenstående algoritme.
C++ // C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function #include using namespace std; int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and subtract their multiples // from result for(int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat / n; returnere resultat; } // Driverkode int main() { int n; for(n = 1; n<= 10; n++) { cout << 'Phi' << '(' << n << ')' << ' = ' << phi(n) << endl; } return 0; } // This code is contributed by koulick_sadhu>C // C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include int phi(int n) { int result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat / n; returnere resultat; } // Driverprogram til at teste ovenstående funktion int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Java // Java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat / n; returnere resultat; } // Driver Code public static void main (String[] args) { int n; for (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by ajit>Python3 # Python3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function def phi(n): # Initialize result as n result = n; # Consider all prime factors # of n and subtract their # multiples from result p = 2; while(p * p <= n): # Check if p is a # prime factor. if (n % p == 0): # If yes, then # update n and result while (n % p == 0): n = int(n / p); result -= int(result / p); p += 1; # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most # one such prime factor) if (n>1): resultat -= int(resultat / n); returnere resultat; # Driverkode for n i området(1, 11): print('phi(',n,') =', phi(n)); # Denne kode er bidraget # af mits>C# // C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and // subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat / n; returnere resultat; } // Driver Code static public void Main () { int n; for (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed // by akt_mit>Javascript // Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi(n) { // Initialize // result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while (n % p == 0) n = parseInt(n / p); result -= parseInt(result / p); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= parseInt(resultat / n); returnere resultat; } // Driverkode for (lad n = 1; n<= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} `); // This code is contributed // by _saurabh_jaiswal>PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi($n) { // Initialize // result as n $result = $n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for ($p = 2; $p * $p <= $n; ++$p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ($n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while ($n % $p == 0) $n = (int)$n / $p; $result -= (int)$result / $p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ($n>1) $result -= (int)$result / $n; returnere $resultat; } // Driverkode for ($n = 1; $n<= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(', $n,') =', phi($n), '
'; // This code is contributed // by ajit Φ>> Produktion
Phi(1) = 1 Phi(2) = 1 Phi(3) = 2 Phi(4) = 2 Phi(5) = 4 Phi(6) = 2 Phi(7) = 6 Phi(8) = 4 Phi( 9) = 6 Phi(10) = 4
Tidskompleksitet: O(Φ n log n)
Hjælpeplads: O(1)
Lad os tage et eksempel for at forstå ovenstående algoritme.
n = 10.
Initialiser: resultat = 10
2 er en primfaktor, så n = n/i = 5, resultat = 5
3 er ikke en primær faktor.
For-løkken stopper efter 3 som 4*4 er ikke mindre end eller lig
til 10.
Efter for loop, resultat = 5, n = 5
Da n> 1, resultat = resultat - resultat/n = 4
Nogle interessante egenskaber ved Eulers Totient-funktion
1) For en primtal p ,
Bevis:
Eksempler:
2) Til to primtal a og b
Bevis:
Eksempler:
3) Til et primtal p ,
streng til heltal i java
Bevis:
Eksempler:
4) Til to tal a og b
Særligt tilfælde : gcd(a, b) = 1
Eksempler:
Særlig situation :
5) Summen af værdier af totientfunktioner af alle divisorer af n er lig med n.
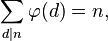
Eksempler:
n = 6
faktorer = {1, 2, 3, 6}
n =
6) Det mest berømte og vigtigste træk kommer til udtryk i Eulers sætning :
Sætningen siger, at hvis n og a er coprime
(eller relativt prime) positive heltal, altså
-enΦ(n)Φ 1 (mod n)
kunstigt neurale netværk
Det RSA kryptosystem er baseret på denne sætning:
I det særlige tilfælde, hvor m er primtal sige p, bliver Eulers sætning til den såkaldte Fermats lille teorem :
-enp-1Φ 1 (mod p)
7) Antallet af generatorer af en endelig cyklisk gruppe under modulo n addition er Φ(n) .
Relateret artikel:
Eulers Totient-funktion for alle tal mindre end eller lig med n
Optimeret Euler Totient-funktion til flere evalueringer
Referencer:
http://e-maxx.ru/algo/euler_function
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euler%27s_totient_function
https://cp-algorithms.com/algebra/phi-function.html
http://mathcenter.oxford.memory.edu/site/math125/chineseRemainderTheorem/
